Time to read: 7 minutes 53 seconds | Published: October 21, 2025
Network security What is network security?
Network security involves using hardware, software, and as-a-service (aaS) solutions to protect edge-to-cloud network infrastructure from cyberattacks, data loss, and misuse.
Network security technology can include firewalls (including next-generation firewalls and hybrid mesh firewalls), intrusion detection and prevention systems, data encryption, and secure network access controls. Effective network security also includes best practices like regular updates, employee training, and incident response planning. These efforts collectively help protect against threats such as viruses, ransomware, phishing attacks, and insider threats while supporting the integrity and availability of network infrastructure.
Network security is essential for enterprises of all sizes and industries. Enterprises that handle sensitive data, use networked systems for business transactions, or are in regulated industries need strong network security to protect against cyber threats and ensure business continuity.

Why do businesses need network security?
Businesses need network security to protect their most important asset—their data. Without effective network security in place, businesses are at increased risk of attacks and hacks.
According to Statista, 328.77 million terabytes of data points are created each day and internet users spend six hours and forty minutes online daily, all facilitated by the network. Protecting network data and connection are of immense importance—a security breach can result in losses over billions of dollars. A recent study by the Ponemon Institute, Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025, reveals, "The global average cost of a data breach in 2025 was USD 4.44 million. [In the U.S.,] the average cost surged by 9% to USD 10.22 million, an all-time high for any region."
Network security helps reduce the potential threat surface of and damage from cybersecurity attacks by proactively monitoring and enforcing edge-to-cloud security policies and enhancing network performance by streamlining digital traffic.
Businesses use network security to:
- Protect corporate data.
- Control network access and availability.
- Detect and prevent intrusions.
- Respond to and address incidents.
- Protect hardware resources, software, and intellectual property.
- Protect data centers and cloud computing.
How does network security work?
Different hardware and software solutions can be deployed on user devices, servers, in data centers, and in the cloud to secure the network. These solutions enable security teams to provide proper network authorization and block potential threats by implementing and enforcing security policies. Ideally, these products are configured in-line with broader business security policies and work with each other to achieve strong network security.
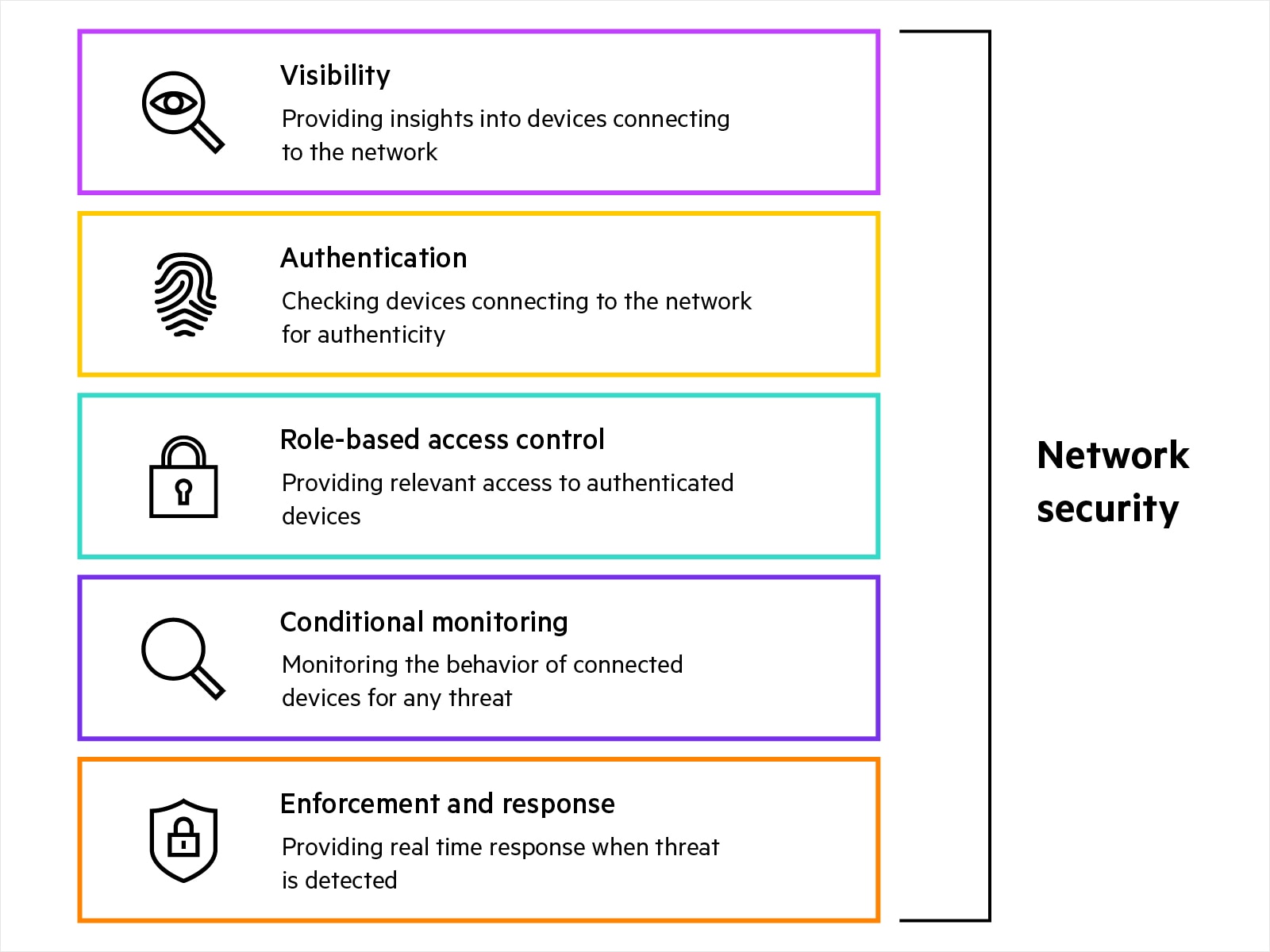
What are the components of network security?
Network security includes physical, virtual, agent-based, and agentless solutions such as:
- Device profiling and visibility: Agent-based and agentless solutions providing visibility into type and behavior of devices connecting to the network. These visibility insights act as the first step in securing the network and help security teams in device discovery, device profiling, custom fingerprinting, and anomaly detection.
- Authentication and authorization: Agent-based and agentless solutions providing role-based authentication for edge devices trying to connect to the network. A NAC (network access control) solution authenticates user or device identity against a wide variety of identity sources, to support robust network security. Policy can be applied that authorizes the subject to access only the resources needed to fulfill its job or function (least-privilege access).
- Role-based access security and policy enforcement: Enforcing least privilege access to the edge devices allows access to only relevant resources or parts of the network by segmenting traffic based on identity or role and associated access permissions.
- Conditional monitoring: Continuous monitoring requires solutions that provide real-time threat telemetry by constantly monitoring edge devices. Different products work individually and together to track edge-device behaviour and flag any potentially malicious activity to network access control (NAC) systems for further action. Continuous monitoring solutions include:
- Unified threat management/IDS/IPS: Intrusion detection provides threat intelligence on malicious activities including command and control, ransomware, phishing, malware, spyware, trojans, and exploit kits. Intrusion prevention detects malicious activities and performs actions like blocking the traffic to protect against malicious activity.
- Web content classification, IP reputation and geolocation filtering: Content filtering blocks specific websites that are potentially harmful. Web content filtering helps identify websites that propagate malware, spam, spyware and phishing attacks, as well as websites with sensitive content such as adult or gambling content. IP Reputation services provide a real-time feed of known malicious IP addresses in multiple categories so IT security administrators can easily identify threats by type. Geolocation filtering services associate source/destination IP addresses with location. It allows organizations to apply policies to permit or drop inbound or outbound communications with countries of concern.
- SIEM or interoperable products: SIEMs help security teams detect, analyze, and respond to security threats.
- Secure SD-WAN: SD-WAN solutions are used to efficiently connect users and applications. A secure SD-WAN solution has built-in security capabilities and works with other elements within the security ecosystem to enforce strong network and application security from edge-to-cloud.
- Enforcement and Response: When malicious activity is suspected of or observed participating in an attack, the NAC (network access control) solution can take either guided or automated attack response to preserve network security. Security teams also deploy different types of firewalls for robust network security enforcement.
- Firewall: A network firewall is hardware or software that restricts and permits the flow of traffic between networks. Network firewalls help prevent cyberattacks by enforcing policies that block unauthorized traffic from accessing a secure network.
- Next gen firewall: Next generation firewalls add advanced capabilities like application-level packet inspection and intrusion prevention to traditional packet-filtering network firewall capabilities.
- Hybrid mesh firewall: A hybrid mesh firewall solution streamlines security across distributed network environments by unifying on-premises, virtual, and containerized firewalls via a single, centrally managed point of control. Hybrid mesh firewall can help eliminate security gaps, reduce the operational burden of firewall management, and enable consistent policy definition and enforcement, visibility, and threat protection regardless of where traffic originates or flows.
In today’s world workers access corporate networks from home, cafés, airports, etc. They also consume a lot of SaaS apps that are not hosted in corporate data centers or private clouds. Besides securing the network, security teams need a robust Security Service Edge (SSE) solution to reduce potential attack surface and improve application security for SaaS and web services.
What are the benefits of network security?
The key benefit of strong network security is defending against cyberattacks. Any business without sufficient network security could be an easy target for cyber attackers. Some other critical benefits to network security include:
- Reducing network disruptions: Businesses can lose money due to network disruption.A strong network security solution can help avoid or reduce potential loss by continuously detecting and neutralizing malware, denial of service, and other cyberattacks.
- Minimizing data breaches: Strong network security protects sensitive and business-critical data from hackers by authenticating all the devices connecting to a network, authorizing proper access based on role and identity, continuously monitoring the devices, and enforcing automated action when malicious activities are detected.
- Enhancing network performance: Robust network security optimizes network performance by segmenting traffic flow through the network, enabling proper bandwidth allocation between critical and common applications, and among employees and guests.
- Building trust: Ensuring that devices connecting to the network have updated posture checks and meet business security policies can support compliance with data privacy and cyber security regulations. Furthermore, the customers of a business with strong network security may feel more comfortable sharing their confidential information since strong network security can protect against many kinds of cyberattacks that can result in data loss and compromises.
Network security and data
Network security is based on four data elements:
- Data access: Data access is controlled by a system that authenticates, authorizes, and accounts for (AAA) users' identification (usually through a PIN or login), grants authorization and permission based on users' function, and logs data changes and records users' network activities.
- Data availability: Data is available to users when it is needed (available on demand); only authorized users can access and use the data.
- Data confidentiality: Data cannot be leaked to or accessed by unauthorized users; data encryption protects data transmission and prevents unathorized access by third parties.
- Data integrity: Data cannot be changed without authorization; it is the assurance that information can only be accessed and modified by those subjects authorized to do so.
Network security and protection
The old network security model of securing the perimeter of a network by solely implementing firewalls is no longer enough. Most threats and attacks originate from the internet (making interfaces to the internet the most critical to secure), while other common sources of threats are compromised users' devices, and roaming peers. Additionally, network complexities and communications undermine security between internal and external environments. Networks are vulnerable to both active and passive attacks, as well as from inside-out and inside-in attacks. Active attacks, such as denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, IP address spoofing (or masquerade attacks), and malware created to target both physical and virtual machines (VMs), are the most complex security threats to manage because they target the control plane (the part of a network that carries signaling traffic and is responsible for routing) of network elements.
Thus the future of network security requires a change in mindset: Security must be ingrained everywhere—in the protocols, the systems, the elements, the provisioning, and in the business surrounding the network.
To better combat and contain security threats in the network, organizations are moving toward a more distributed architecture, with detection and enforcement enabled everywhere. As the threat environment morphs and accelerates, automated and centralized security polices with decentralized enforcement on switches and routers can be driven by dynamic and real-time security updates. Using software-defined controls, organizations can detect threats and enforce security policies with a high level of automated security, unified threat detection, and real-time protection.
Today, those in charge of network security must assume zero trust among network elements, and operate their network as a domain where every element—not just those at the perimeter—can activate zero trust security principles.
HPE and network security
HPE Networking secure AI-native networking offers performance and control built on integral security. Now organizations have a common foundation for networking and security operations to achieve shared universal visibility, global policy management, end-to-end enforcement, and AI-powered automation—connecting and protecting all users, devices, apps, and data across the entire infrastructure.
HPE Aruba Networking Central NetConductor provides an end-to-end, cloud-native network automation and orchestration solution that automatically configures LAN, WLAN, and WAN infrastructure across branch, campus, and data center to deliver optimal network performance while defining and enforcing granular security policies that are the foundation of zero trust and SASE architectures. Central NetConductor comprises: Client Insights to deliver AI-powered device visibility and profiling; Central NAC to deliver cloud-based authentication; Policy Manager and CX Switches and Gateways for cloud-based NAC and in-line policy definition, distribution, monitoring and enforcement.
HPE Aruba Networking also offers enterprise grade network access control with ClearPass. ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) offers profiling for device visibility, supports a wide range of authentication and authorization protocols, integrates with Policy Enforcement Firewall for dynamic segmentation, is compatible with a large ecosystem of 3rd-party vendors for conditional monitoring, and provides real-time security enforcement and response based on enterprise security protocols.
The HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-Branch solution is equipped with IPS, IDS, Web content classification, IP reputation and geolocation filtering functionalities.
HPE complements its strong network security solutions with HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen10 servers and HPE Pensando SmartNIC, that allows organizations to experience hardware-based networking and security acceleration. Incorporating hardware telemetry, firewalling, encryption, and micro-segmentation, this offering simplifies data encryption through API.
HPE Juniper Networking connected security
HPE Juniper Networking Connected Security automates security coverage from endpoint to edge and every cloud in-between. HPE Juniper Networking provides the window to see who and what is on your network and enforce across all connection points. To help safeguard your existing security investment, HPE Juniper Networking solutions are open so that you can build on security solutions and infrastructure you already have in place.
To deliver consistent security policies across multi-cloud infrastructure, the HPE Juniper Networking SRX Series hybrid mesh firewall solution, powered by Security Director Cloud, enables organizations to create and enforce consistent security policies across mixed on-premises and cloud environments and seamlessly transition to new architectures. The solution also expands zero trust across the network from edge to data center to applications and microservices.
To protect the growing digital universe, organizations must devise and follow a thorough, multi-layered, defense-in-depth approach to security by considering all information traversing the network and in the cloud, and not just threats solely identified at the perimeter and edge.