Network access control What is NAC (Network Access Control)?
Controlling access to digital resources is a critical IT security capability for organizations. Network access control (NAC) solutions enable IT to authorize or prevent users and devices from accessing resources on the network. NAC plays an important part in delivering least-privilege access to resources that is foundational to Zero Trust Security strategies.
Time to read: 5 minutes 36 seconds | Updated: October 31, 2025
Table of Contents
NAC explained
Network access controls restrict users and devices from reaching resources based on rules established by IT. Much like door locks and security badges keep intruders from accessing physical organizational resources like buildings and offices, network access controls protect networked digital resources from unauthorized access.
Why is NAC important?
- Security—Network access controls protect resources from tampering and theft by malicious actors. NAC solutions ensure that only users and devices with proper permissions can access the network and networked resources. Furthermore, some NAC solutions can identify subjects that may be participating in an attack and quarantine or block that subject’s access pending further investigation. This functionality can prevent the spread of attacks.
- Privacy—Organizations are managing greater volumes and varieties of data than ever before. Some of this data is sensitive and/or confidential. Network access control solutions allow organizations to define who, what, when, and how data can be accessed on the network, to reduce risk of breach.
- Compliance—Regulated organizations often need to comply with data privacy and data protection mandates, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX). NAC solutions can help organizations comply with these mandates by restricting access to data, keeping traffic secure and separate, and providing logging and reporting for audits.
How does NAC work?
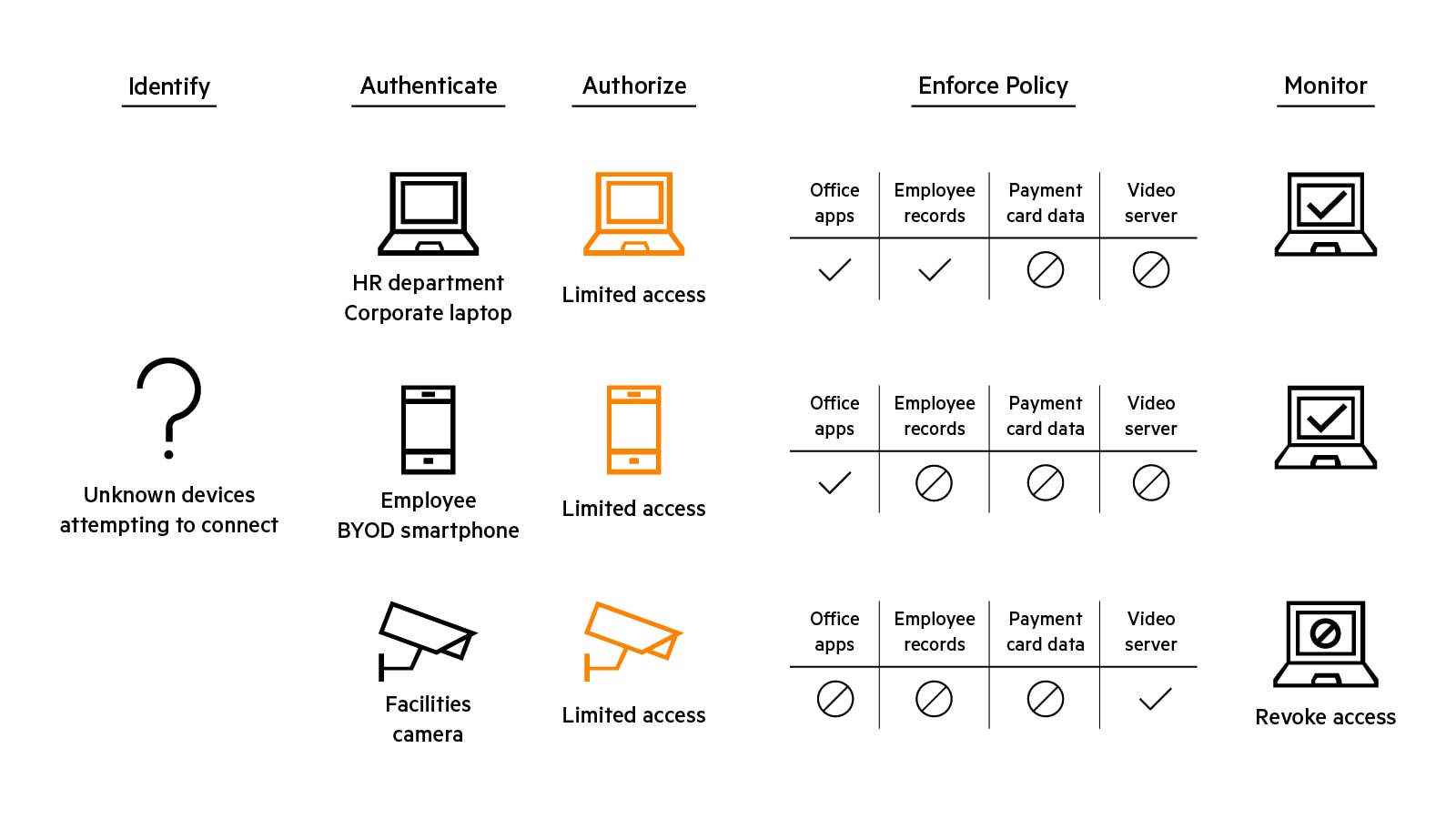
Network access control is predicated on the concept that different users and devices (subjects) are granted different types of access based on their needs. Granularity refers to the level of detail with which a subject, its needs, and its associated access permissions can be defined and enforced. Highly granular network access controls are a key component of Zero Trust Security approaches that limit a subject’s access to just the resources needed to do their job or fulfill their function.
To protect resources effectively, network access control solutions must provide several inter-related capabilities delivered through a mix of technologies.
What are examples of NAC?
NAC solutions provide secure access to resources throughout an organization. For example, a hospital uses a NAC solution to profile, secure and manage connectivity of authorized IoT devices, while excluding others. A fulfillment center uses a NAC solution to authenticate every wired and wireless device that accesses the network—such as robots—and implement consistent role-based policies. A school system uses a NAC solution to authenticate students, teachers, staff and guests, and enable granular segmentation of traffic based on defined rules.

How do I select a NAC solution?
When choosing a NAC solution, consider the following:
- Interoperability and vendor-neutral features to avoid costly add-ons and vendor lock-in
- Demonstrated ability to keep traffic secure and separated
- Service availability to support maximal uptime and non-stop operations
- Scalability to support hundreds of thousands of concurrent endpoints
- Market leadership and designations that recognize capability to reduce cyber-risk, such as Cyber CatalystSM by Marsh designation
NAC elements
Capabilities | Function | Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Knowing who and what is on the network at any given time. | Physical or virtual data collectors: active (NMAP, WMI, SNMP, SSH) and passive (SPAN, DHCP, NetFlow/S-Flow/IPFIX) discover methods:AI/ML-assisted device profiling; deep packet inspection. |
| Authentication | Ascertaining with confindence that a user or device is who/what is attests to be. | 802.1x authentication; EAP-TLD, RADIUS, TAC-ACS; multi-factor authentication; certificates. |
| Policy definition | Defining rules for users and devices regarding resource they can access, and how resources can be accessed. | Rule-writting tools, which can include contextul parameters like role, device type, authentication method, device health, traffic patterns, location and time-of-day. |
| Authorization | Determining the appropriate rules for the authenticated used or device. | |
| Enforcement | Alloying, denying, or revoking and authenticated user or device's access to a resource based on appropriate policy. | Integration and bidirectional communication with firewalls and other security tools. |
What is NAC used for?
NAC solutions like HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass can address several secure connectivity use cases within organizations:
| NAC for guests and temporary workers | ClearPass Guest makes it easy and efficient for receptionists, event coordinators, and other non-IT staff to create temporary network access accounts for any number of guests per day. ClearPass Guest also offers a customized self-registration portal, which allows visitors to create their own credentials that are then stored in ClearPass for pre‑determined amounts of time and can be set to expire automatically. |
| NAC for bring your own device (BYOD) | ClearPass Onboard automatically configures and provisions mobile devices, enabling them to securely connect to enterprise networks. Workers can self-configure their own devices by following guided registration and connectivity instructions. Unique per-device certificates are applied to ensure that users can securely connect their devices to networks with minimal IT interaction. |
| NAC for endpoint security posture assessment | ClearPass OnGuard performs endpoint/device posture assessment to ensure security and compliance requirements are met prior to devices connecting to the corporate network, which can help organizations avoid introducing vulnerabilities into their IT environments. |
| NAC for Internet of Things (IoT) devices | ClearPass Device Insight provides full spectrum visibility of network-connected devices with risk-scoring and machine learning to identify unknown devices and reduce time-to-identification. ClearPass Device Insight also monitors the behavior of traffic flows for added security. |
| NAC for wired devices | ClearPass OnConnect provides secure wired access control for devices like printers and VoIP phones that do not authenticate using 802.1x techniques. |
| Cloud-native NAC | HPE Aruba Networking Central Cloud Auth integrates with common cloud identity stores to deliver seamless cloud-based onboarding and secure role-based policy for users and devices. |
FAQs
What are the problems network access control (NAC) address?
Modern enterprise networks face increasing pressure from the rise of wireless access, mobility, Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies, social media, and cloud computing. These trends dramatically expand the network’s attack surface, making it more vulnerable to unauthorized access, data breaches, and digital exploitation. Network access control (NAC) using 802.1x provides a robust defence by enforcing ingress security—ensuring that only authenticated and authorized devices can connect to the network.
What can you do with network access control?
NAC is a critical component of Network Security offering the following essential usage:
- Pre-admission control: Blocks unauthenticated messages.
- Device and user detection: Identifies users and devices with pre-defined credentials or machine IDs.
- Authentication and authorization: Verifies and provides access.
- Onboarding: Provisions a device with security, management, or host-checking software.
- Profiling: Scans endpoint devices.
- Policy enforcement: Applies role and permission-based access.
- Post-admission control: Enforces session termination and cleanup.
802.1X provides L2 access control by validating the user or device that is attempting to access a physical port.
How does network access control implement a Zero trust security?
The 802.1X NAC operation sequence is as follows:
- Initiation: The authenticator (typically a switch) or supplicant (client device) sends a session initiation request. A supplicant sends an EAP-response message to the authenticator, which encapsulates the message and forwards it to the authentication server.
- Authentication: Messages pass between the authentication server and the supplicant via the authenticator to validate several pieces of information.
- Authorization: If the credentials are valid, the authentication server notifies the authenticator to give the supplicant access to the port.
- Accounting: RADIUS accounting keeps session records including user and device details, session types, and service details.
- Termination: Sessions are terminated by disconnecting the endpoint device, or by using management software.
What is the role of NAC in Universal ZTNA (UZTNA)?
Network access control (NAC) plays a foundational role in Universal ZTNA (UZTNA) by providing device-level authentication, posture validation, and access enforcement—especially for on-premises and IoT environments. While traditional NAC secures network entry points, UZTNA extends this by integrating NAC capabilities into a cloud-native Zero Trust framework, enabling fine-grained, identity-based access to applications and resources across both local and remote environments.