WLAN What is WLAN?
A WLAN connects local network nodes using radio technology rather than wired connections. Wi‑Fi is a specific type of WLAN that conforms to the IEEE standard 802.11 and relies on access points (APs) to connect to clients and IoT devices using the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and the 6 GHz band. Other types of WLANs may operate using different bands.
Time to read: 3 minutes, 20 seconds | Updated: January 26, 2026.
Table of Contents
WLAN explained
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is a type of Local Area Network (LAN) that uses wireless communication to connect any type of network client or device. The other type of LAN is a wired LAN.
Is WLAN the same as Wi‑Fi?
Wi‑Fi networks are a type of WLAN but not all WLANs are Wi‑Fi. Other radio transmissions that connect local network nodes are also WLANs. However, Wi‑Fi is the type of WLAN that is most widely used.
Why WLAN?
- Growth in mobility and IoT: According to IDC, IoT is forecast to growth to 41.6bn devices by 2025, generating 79.4 zettabytes of data. Mobility, roaming, cloud, cellular offload, device onboarding, and security issues mean that Wi‑Fi needs to support convergence, higher throughput, and more efficient RF utilization.
- Growth in diversity and bandwidth demands of applications: Latency sensitive video applications are on the rise with 45%/year growth through 2023.
- Growth in user expectations: Low tolerance for poor network performance leads to executive pressure. The network and applications must be accessible from anywhere, secure, and always on.
What is the role of a wireless controller in WLANs?
Wireless controllers, sometimes referred to as gateways when operating in a cloud-managed environment, provide high-performance access, resiliency, and security across the WLAN, LAN, and SD-WAN.
Next generation WLAN controllers deliver:
- Performance at scale to support thousands of APs and devices with 24×7 reliability, zero touch provisioning, and live upgrades thereby reducing the need for on-site IT support.
- Security enforcement with granular role-based rules and dynamic segmentation.
- L2/L3 roaming across VLANS to allow seamless handoffs and improved user experience.
- N+1 or NxN redundancy for greater performance and scale.
What is the difference between a WLAN and a VLAN?
If there are too many devices on a single LAN, it can create congestion and bottlenecks. To eliminate broadcast overhead and improve security and performance, the network can be divided into multiple virtual LANs or VLANs.
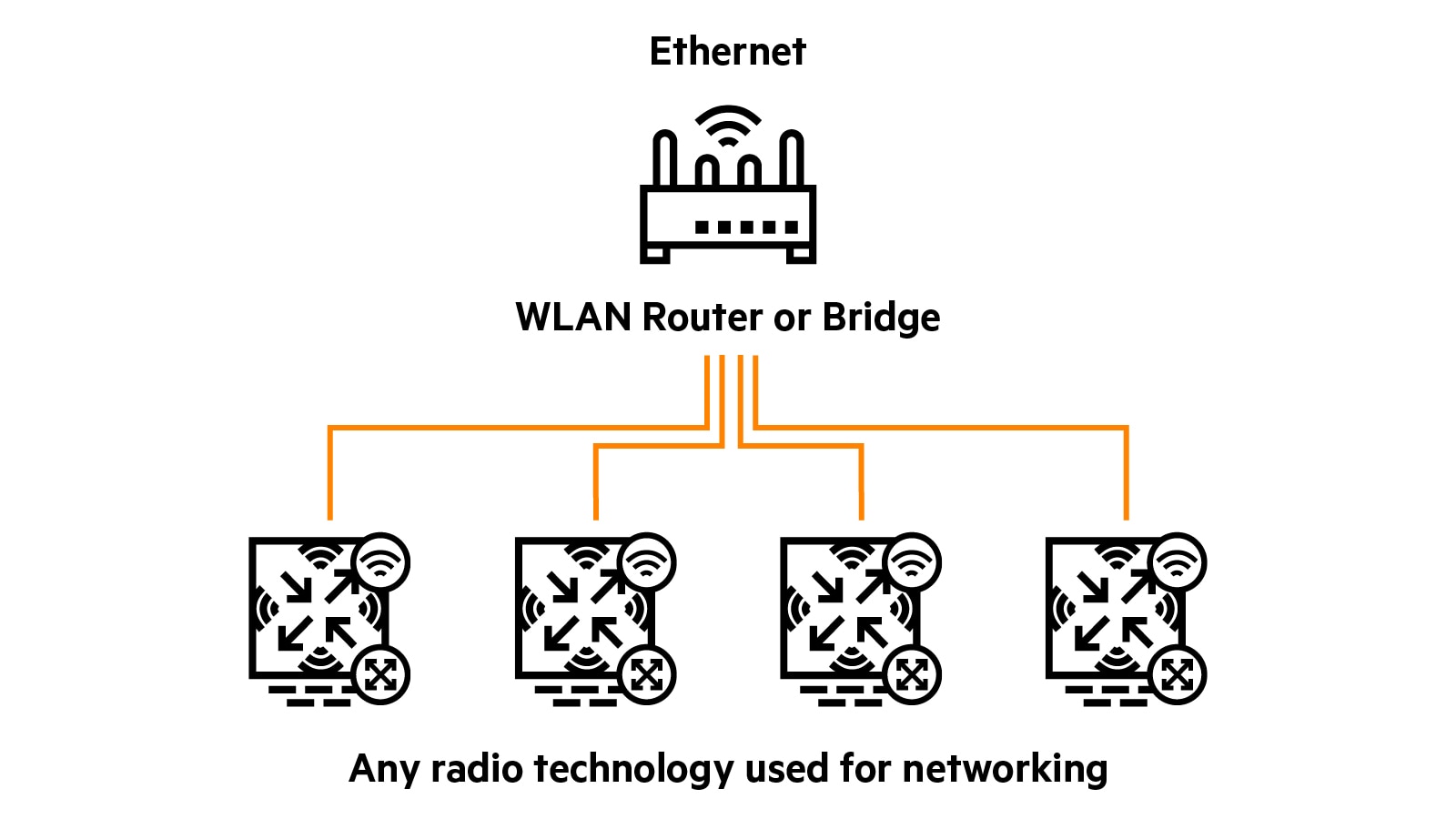
WLAN overview
WLAN is a general term referring to any wireless technology. Wi‑Fi is specifically defined by IEEE and uses access points (APs) and 802.11 clients.

HPE Aruba Networking WLAN controllers and gateways
HPE Aruba Networking offers a full portfolio of WLAN controllers and gateways to meet the needs of mid-sized branches and large campus environments. Recognized as a leader in WLAN, HPE Aruba Networking continues to innovate with the 9000 Series Gateways for branches and small campuses and the 9200 Series Gateways for larger environments.
- 9200 Series.
- 9000 Series.
- 7200 Series.
- 7000 Series.
- Mobility Controller Virtual Appliance.
FAQs
How does WLAN work?
A wireless LAN (WLAN) connects local network nodes using radio technology rather than wired connections. Wi-Fi is a specific type of WLAN that conforms to the IEEE standard 802.11 and relies on access points (APs) to connect to clients and IoT devices using the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and the 6 GHz band. Using a gateway, a WLAN can provide access to the internet.
What are the benefits of using a WLAN?
WLAN benefits include mobility for users, scalability to accommodate increased numbers of users quickly, IoT device connectivity, precision location-based services, and cellular offload.
What are the advantages of using WLAN over LAN?
The key advantage of WLAN is the mobility and flexibility of allowing users and IoT devices to connect to the network wirelessly from anywhere within the coverage area, without the cost or complexity of running cables. This wireless connectivity not only simplifies installation and network expansion but also supports rapid scaling as user demands grow, making WLAN an ideal solution for dynamic environments. WLANs also facilitate seamless integration of IoT devices, enable advanced services such as precision location tracking, and efficiently offload cellular.
What security measures should I take for my WLAN?
To strengthen security, leverage the Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and Wi-Fi 7 (802.3be) access point capabilities such as WPA3 that provide stronger encryption and authentication, and Enhanced Open that protects credentials/keys storage for guest access. Role-based security, policy enforcement firewalls, and dynamic segmentation are additional security features that help enable a more secure WLAN.
What are common issues with WLAN connections?
Common Wi-Fi issues include poor performance while roaming, spotty connectivity in high density environments, coverage holes across sites, limited IoT device connection choices, and high latency for video and streaming services. Other challenges include interference between neighboring Wi-Fi networks or electronic devices, outdated firmware or drivers impacting compatibility, and misconfigured settings that can hinder seamless access. In addition, insufficient network capacity may cause congestion during peak usage, while environmental obstacles such as walls or reflective surfaces can degrade signal strength and reliability throughout the coverage area. more secure WLAN.