SASE What is SASE?
SASE combines comprehensive WAN capabilities including SD-WAN, routing, and WAN optimization with cloud-delivered security services or SSE (Security Service Edge) such as SWG (secure web gateway), CASB (cloud access security broker), and ZTNA (zero trust network access).
As users connect from anywhere and access sensitive data in the cloud, SASE brings a more secure and flexible way to connect by not backhauling application traffic to a data center. Instead, SASE intelligently steers the traffic to the cloud and performs advanced security inspection directly in the cloud.
SASE responds to today’s critical IT challenges, including accelerated cloud migration, modernizing aging network infrastructure, supporting hybrid work, and securing the rapidly expanding attack surface created by IoT devices. It also safeguards sensitive data against leakage and compromise, while strengthening defense against the rising volume and sophistication of cyber threats.
Time to read: 9 minutes 14 seconds | Updated: October 17, 2025
Table of Contents
How does SASE work?
SASE is the combination of an advanced SD-WAN edge deployed at the branch and comprehensive cloud-delivered security services (SSE).
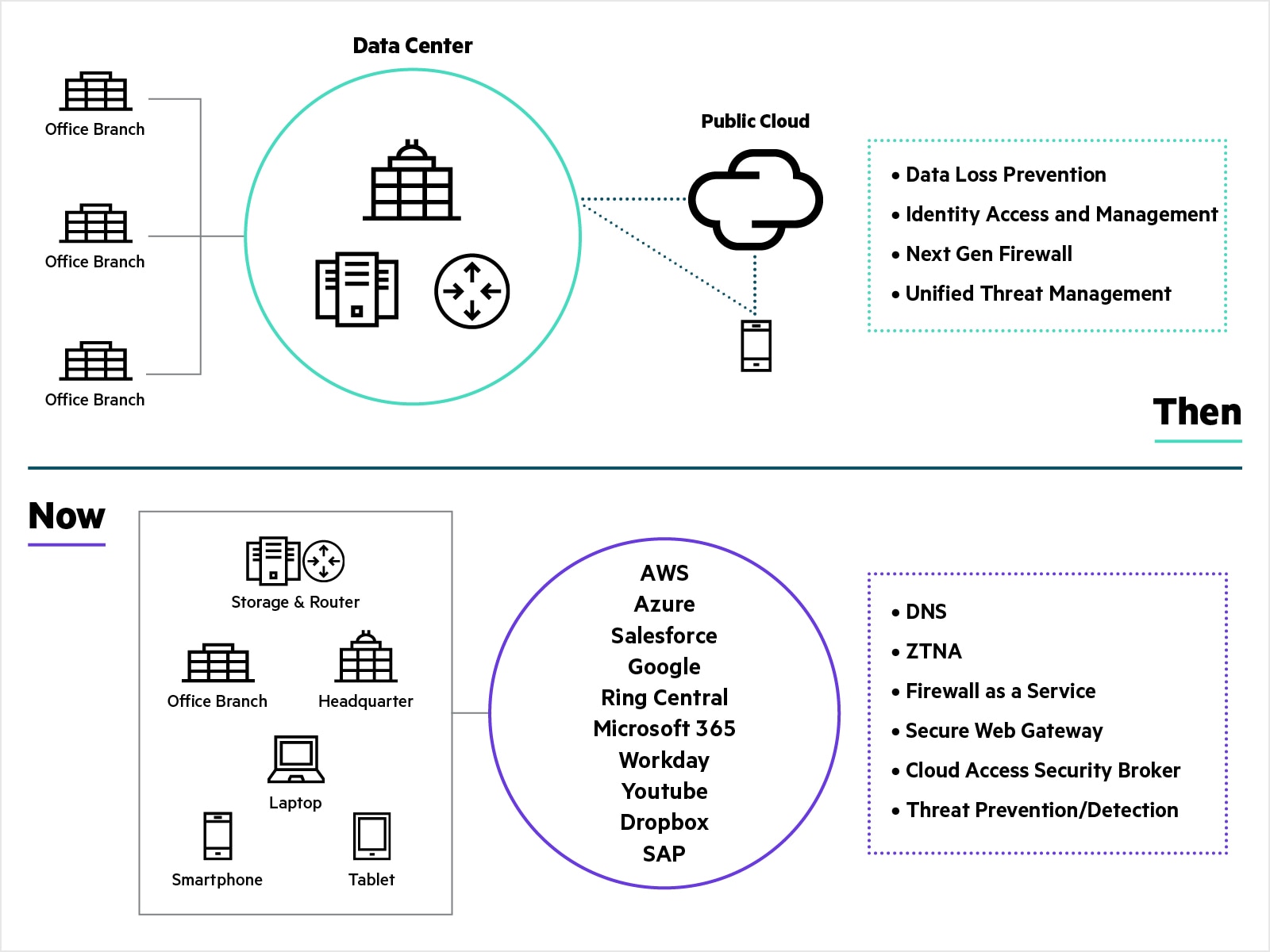
Traditionally, all application traffic from branch locations traversed over private MPLS services to the corporate data center for security inspection and verification. This architecture was appropriate when applications were hosted exclusively in the corporate data center. Now that more applications and services have migrated to the cloud, the traditional network architecture falls short. Because internet-destined traffic must first travel through the data center and corporate firewall before reaching its destination, application performance and user experience suffers.
With the increase in remote workers connecting directly to cloud applications, traditional perimeter-based security is insufficient. By transforming WAN and security architectures with SASE, enterprises can achieve direct, secure access to applications and services across multi-cloud environments, regardless of location or the devices used to access them.
What are the components of SASE?
The main components of SASE are advanced SD-WAN and comprehensive cloud-delivered security (Security Service Edge or SSE).
There are key advanced SD-WAN capabilities to fully enable SASE:
- Seamless integration with an SSE solution to form a unified, consistent SASE architecture.
- First-packet application identification to enable granular steering of traffic to SSE based on security policies.
- Best path selection by exploiting SD-WAN path diversity and automatically selecting the closest SSE PoP (point of presence).
- Tunnel bonding to combine multiple links and support automated failover.
- WAN optimization and FEC (forward error correction) to overcome the latency effects of WAN and mitigate the effects of internet and wireless links that often suffer from packet loss and jitter.
- Multi-cloud networking to provide end-to-end connectivity with public and private clouds.
- Built-in firewall with advanced security capabilities such as IDS/IPS, DDoS protection and role-based segmentation for advanced threat protection in branch locations.
There are key SSE capabilities to fully enable SASE:
- ZTNA or zero trust network access: assumes that no user can be trusted by default and supports least privileged access. It provides secure access to remote users.
- CASB or cloud access security broker: protects sensitive data in cloud applications by enforcing security policies.
- SWG or secure web gateway: protects organizations from web-based threats using several techniques such as URL filtering and malicious code detection.
- FWaaS or firewall as a service: provides firewall functionality in the cloud to analyze the traffic from multiple sources.
- Other security services such as DLP (data loss prevention), RBI (remote browser isolation) and sandboxing.
What are the benefits of SASE?
SASE isn’t just the latest buzzword. There are important business benefits enterprises realize from a SASE architecture.
- Enhanced security: As organizations shift to a cloud-first approach, SASE enforces security policies consistently across all traffic and locations, with inspection performed directly in the cloud. It safeguards remote access and protects enterprise data from cyber threats, while minimizing the attack surface and enhancing threat detection and response.
- Improved business productivity and customer satisfaction: With SASE, organizations can streamline their network infrastructure based on advanced SD-WAN capabilities. By eliminating the limitations and complexity of conventional router-based networks, SASE introduces the agility needed for digital transformation, resulting in notable enhancements in both application performance and reliability.
- Zero trust security model: SASE embraces the zero trust security model by requiring continuous verification of user identity before granting access to resources. Zero trust is particularly relevant in today’s threat landscape, where traditional security models are no longer sufficient to protect against sophisticated cyber threats.
- Simplified management and reduced complexity: SASE streamlines deployment, as well as network and security management. It consolidates multiple, disparate networking and security functions (like SD-WAN, SWG, CASB, and FWaaS) into a single platform. This convergence reduces the need for managing a sprawl of vendor-specific hardware appliances and point solutions.

How does SASE protect cloud-first enterprises against cyber threats?
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, and workforces become increasingly distributed, enterprises are turning to SASE security to protect their users, data, and applications. By converging advanced SD-WAN and cloud-delivered security services such as ZTNA, SWG, and CASB, SASE provides a unified architecture designed to reduce complexity and enhance protection. With security enforcement happening directly in the cloud, SASE provides consistent policy application, reduces backhauling delays, and provides seamless secure access to applications, whether they reside in private data centers, public clouds, or SaaS platforms.
These capabilities enable organizations to detect threats and stop them from gaining a foothold in the network. As a result, safeguarding user identities, applications, and infrastructure becomes easier.
A SASE architecture mitigates cyber security risks for cloud-first organizations and ultimately improves security while reducing complexity and streamlining management.
Why should I consider SASE?
- Enable and secure hybrid working: As employees connect from anywhere and from any device, ZTNA provides consistent policy enforcement and access control for users and devices. It supports least privilege access and verifies that no user is trusted by default. Unlike a VPN that gives broad access to the corporate network, ZTNA limits user access to only specific applications or microsegments that have been approved for the user.
- Enforce zero trust everywhere with universal ZTNA: Universal ZTNA (universal zero trust network access or uZTNA) extends zero trust principles to on-premises locations and IoT devices by integrating SASE with AI-powered NAC capabilities. This integration enables comprehensive visibility and monitoring of all network-connected devices, including IoT. With identity-based segmentation, universal ZTNA facilitates that users and devices can only access network resources appropriate to their roles. The system continuously monitors network activity, allowing real-time adjustments to access permissions and rapid detection of suspicious or malicious behavior.
- Optimize performance for global and distributed users: SASE leverages a globally distributed cloud architecture and edge computing, enabling users to connect to the nearest PoP (point of presence). This reduces latency and optimizes application performance, especially for users in remote locations.
- Adopt cloud and SaaS applications: SASE enables direct, secure access to cloud applications (e.g., AWS, Microsoft 365, Salesforce) without backhauling traffic through a centralized data center. It optimizes performance through edge computing and SD-WAN while providing security services like CASB to control cloud app usage and protect data.
- Safeguard users against web-based threats: To protect organizations against web-based threats such as ransomware and phishing, SWG monitors and inspects traffic through URL filtering, malicious code detection, and web access control, establishing policies that restrict access to specific categories of websites, including adult content, gambling platforms, and sites known to pose significant risks.
- Secure access to SaaS apps: When users can access both approved and unapproved SaaS applications, a CASB (cloud access security broker) provides visibility into these activities, identifies shadow IT, and enforces organizational SaaS policies, safeguarding sensitive data from potential exposure.
- Protect data and improve compliance: In addition to CASB, SASE includes DLP capabilities, helping organizations monitor user activity and control the movement of sensitive data. Its unified platform also simplifies auditing and reporting, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
- Connect and secure branch offices: Traditional architectures often use MPLS links to connect branch offices to headquarters. In this architecture, cloud traffic must be backhauled to the data center to perform a security inspection, which increases latency, and therefore impacts application performance. With the SD-WAN part of SASE, organizations intelligently steer traffic to the cloud, directly from branch offices, and implement a robust and flexible way to connect branch offices to headquarters. Advanced secure SD-WAN solutions with a built-in next-generation firewall can even replace legacy branch firewalls providing capabilities such as IDS/IPS and DDoS protection.
What is AI-powered unified SASE?
An AI-powered unified SASE platform streamlines the complexity associated with managing multiple security components. This integrated architecture not only simplifies deployment but also provides unified security policies, centralized management, and consistent zero trust access. Key capabilities include:
- Cloud-native architecture and scalability: Designed with a cloud-native architecture, leveraging the scalability and agility of cloud computing. This architecture enables organizations to dynamically allocate resources based on traffic demand, enabling a more efficient and adaptable network.
- Global network presence: Provides a global network presence through geographically distributed Point of Presence (PoPs) to offer consistent performance and low latency, regardless of user location. It simplifies the management of these points of presence, eliminating the need for multiple points of presence required by a multivendor SASE approach.
- Unified policy management: Manages all security policies from a single interface, streamlines operations, reduces complexity, and helps organizations to deploy and enforce consistent policies effectively.
- Centralized UI, comprehensive dashboards: Provides IT teams with the ability to manage all network and security operations in a centralized user interface, with enhanced visibility into network traffic, security events, and policy enforcement. It enhances reporting capabilities, providing organizations with the means to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- Combined SASE capabilities: Organizations can easily combine multiple SASE capabilities to enhance their security posture and inspect traffic in a single pass. SSL inspection is performed only once, improving performance and reducing complexity. Furthermore, by combining SWG and CASB with DLP, organizations can better monitor user activities to protect sensitive data from leaking out and enforce more granular controls over web access.
- AI-driven: With its AI capabilities, an AI-powered unified SASE solution improves visibility into connected users and devices and enables adaptive access control. It automates common troubleshooting activities and diagnoses common network issues, while providing predictive analytics to anticipate future threats and performance issues.
Single or multivendor SASE?
Networking and security, while heavily interrelated, are two different and very complex domains of expertise. Security evolves rapidly to provide protection against ever-changing cybersecurity risks while wide area networking is about providing fast, robust, and flexible connections. The real power of a SASE architecture is realized when combining advanced WAN edge functions with comprehensive SSE security services delivered in the cloud.
The choice to select a single or multivendor solution can vary depending on existing security and WAN requirements. A tight integration of SSE and SD-WAN in a single-vendor SASE platform provides organizations with many benefits including faster deployment, centralized management, consistent security policies, and the ability to adapt seamlessly to the evolving threat landscape. A multivendor approach is recommended for organizations preferring to adopt SASE with their choice of security services or to integrate with an existing security ecosystem. In this multivendor environment, it is critical to choose an SD-WAN that automates orchestration with third-party SSE solutions to decrease deployment time and reduce management complexity.
HPE and SASE
HPE accelerates the path to SASE with an edge-to-cloud zero trust framework. Unlike siloed zero trust products, our unified platform brings together SD-WAN, SSE, and NAC to enforce consistent policies for every user and device—on-premises or remote.
The SSE portfolio delivers ZTNA, SWG, CASB, and DLP, all managed from a single interface, while our cloud-native NAC extends zero trust to all devices—even unmanaged or IoT—through AI-powered observability, authentication, and dynamic segmentation, providing secure access and consistent enforcement across diverse environments.
Our AI-driven secure SD-WAN solutions combine advanced networking features such as tunnel bonding, best path selection, WAN optimization, and multi-cloud networking with built-in security, including next-generation firewall, IDS/IPS, adaptive DDoS defense, URL filtering, and role-based segmentation. They integrate natively with SSE for a complete unified SASE architecture, or with third-party SSE partners for an open, flexible approach.
FAQs
Why is SASE essential for a cloud-first strategy?
Organizations embracing a cloud-first approach need more than traditional networking and security tools to keep pace with evolving demands. SASE plays a critical role in supporting this transformation by delivering secure, reliable, and high-performance connectivity for remote users, branch offices, and IoT devices. With integrated zero trust principles, SASE provides least-privilege access to applications and mitigates risks of unauthorized access or lateral movement within the network. Its combination of SD-WAN efficiency and cloud-native security makes SASE the foundation for modern, scalable, and secure enterprise networks.
What problems does SASE solve?
The IT landscape has changed radically in just a few years. Not long ago, many business applications sat in corporate data centers, accessed by employees through the corporate network. Security was enforced within a clear perimeter. Today, with cloud adoption, IoT, mobility, and remote work, that perimeter has dissolved. Security and networking must now converge into a unified, cloud-delivered architecture.
What is the difference between SASE vs. SSE?
SASE is a comprehensive framework that combines both networking (e.g., SD-WAN) and security services (e.g., SWG, CASB, ZTNA) into a single cloud-native solution designed to securely connect distributed users, devices, and locations. In contrast, SSE (Security Service Edge) is a subset of SASE that focuses solely on security services without including the networking aspects, such as SD-WAN. SSE secures access to cloud services, private applications, and the internet but leaves network management and optimization to other solutions. Essentially, SASE covers both network and security while SSE is limited to security functions only.
Is SASE cloud-based?
Yes, SASE is cloud-based by design. It integrates networking and security services into a unified, cloud-native platform. This cloud-centric approach allows SASE to provide scalability, flexibility, and centralized management for businesses with distributed workforces, multiple branch offices, and cloud environments.
Does SASE prevent backhauling to the data center?
Yes, one of the key benefits of SASE is that it reduces the need for traffic backhauling to the data center, which is a common issue in legacy network architectures. A reduction in backhauling decreases the amount of redundant traffic traveling across the network, which frees up bandwidth, reduces latency, and improves overall network efficiency.
How does SASE improve remote work security?
SASE improves remote work security by unifying networking and security into a cloud-delivered service. It protects remote users with ZTNA, validating that only authenticated users and devices reach applications. SWG blocks malicious websites, while CASB enforces SaaS policies. Data loss prevention (DLP) safeguards sensitive information. By integrating these capabilities with SD-WAN, SASE delivers secure, seamless access to apps from any location, reducing risks for hybrid and remote workers.