Next Gen Firewall What is a Next Gen Firewall (NGFW)?
A next generation firewall (NGFW) permits or blocks traffic between networks. Next generation firewalls add advanced capabilities like application-level packet inspection and intrusion prevention to traditional packet-filtering network firewall capabilities.
Table of Contents
Next generation firewalls explained
A next generation firewall can also be called a next gen firewall, nextgen firewall, or nexgen firewall. Network firewalls act by analyzing traffic between networks and allowing or denying passage of traffic based on defined firewall policies relative to traffic characteristics. Next generation firewalls can ingest information from other systems as well as inspect more characteristics of traffic to enforce firewall policies at higher order Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) communication layers than a traditional firewall. The additional information and deeper level of inspection utilized by next gen firewalls enables them to identify and prevent attacks.
What are next generation firewall features?
Next generation firewalls have more sophisticated features than a traditional, or legacy, network firewall. Here are some common next generation firewall features:
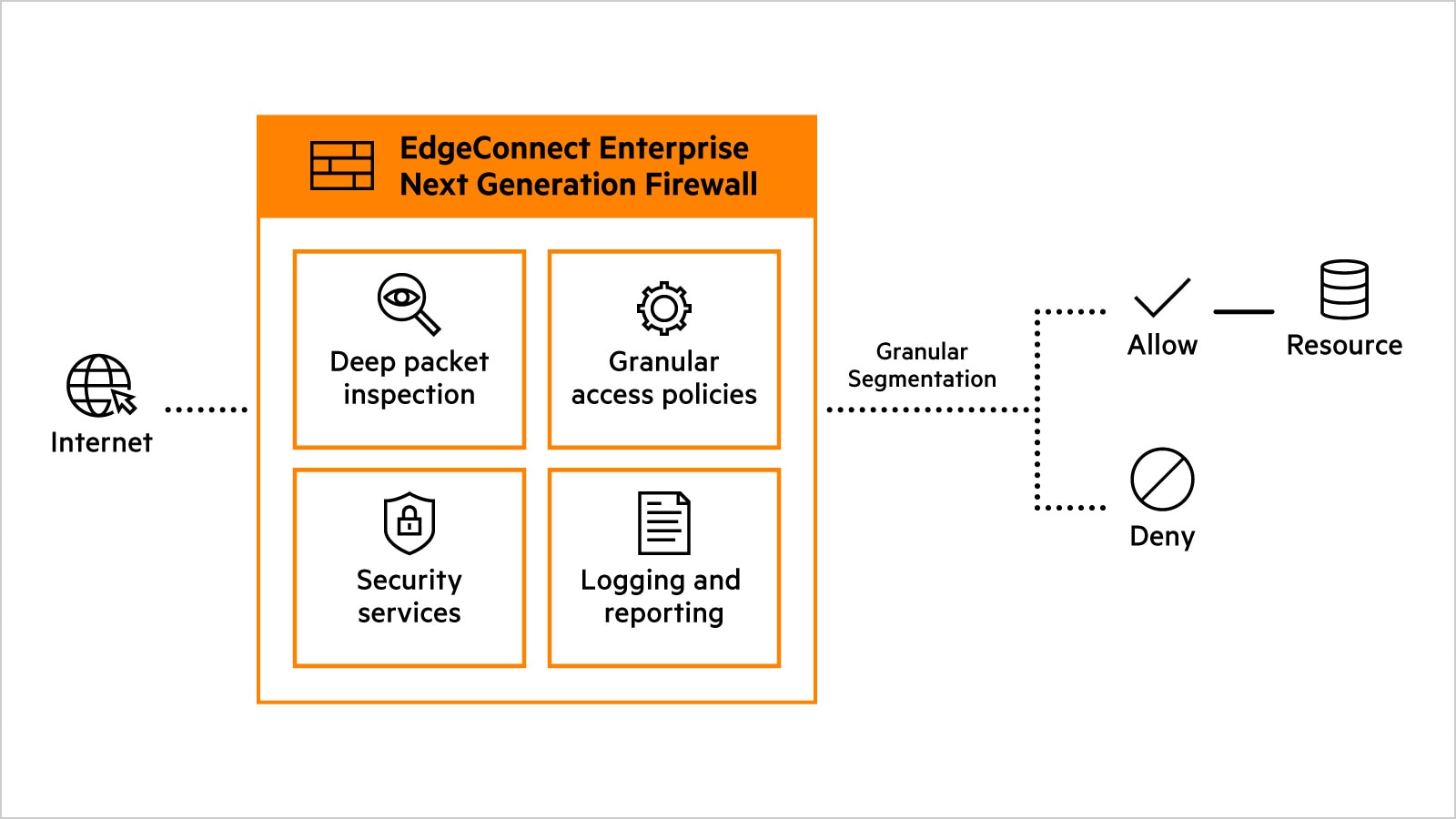
- Deep packet inspection — Network firewalls examine data within the four TCP/IP communication layers (from highest to lowest): application, transport, IP/network, and hardware/data link. Next gen firewalls can inspect traffic at higher order TCIP/IP communication layers, including the application layer. This provides next generation firewalls with application awareness, e.g., context about which application traffic is transiting to and from, and baselines of expected user and application behavior against which to compare transit patterns.
- Intrusion detection and intrusion prevention — Inspecting traffic at higher order TCIP/IP layers enhances next gen firewalls’ ability to detect and prevent cyberattacks. Nextgen firewalls can monitor for potentially malicious activity based on specific behavior signatures or anomalies and then block suspicious traffic from the network. These capabilities are referred to as intrusion detection services (IDS) and intrusion prevention services (IPS).
- Distributed denial of service protection — Denial of service (DoS) attacks are malicious attempts to shut down a service by intentionally flooding the service with illegitimate requests, rendering the service unable to respond to legitimate requests from users. Distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks use multiple computers to generate the flood of illegitimate requests. Next gen firewalls are better able to detect and prevent these sorts of attacks than traditional firewalls because next gen firewalls are stateful. Statefulness enables the firewall to check more characteristics of connection requests against those of established connections, which aids in the detection of illegitimate requests, even when they may be formed differently or coming from different computers.
What are the benefits of next generation firewalls?
Next generation firewalls offer several benefits, including:
- Enhanced protection against cyber threats — Next gen firewalls can inspect and analyze traffic more comprehensively than traditional firewalls, which helps them detect and prevent a greater variety of cyber attacks than a traditional firewall. For example, next gen firewalls can detect traffic maliciously targeting the network and prevent the intrusion by quarantining or blocking the traffic.
- Support for regulatory compliance mandates — Next gen firewalls prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive resources within the network—an important requirement for data privacy and protection regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act in the U.S., and the General Data Protection Regulation in the EU.
- Streamlined network architecture — Next gen firewalls provide advanced threat protection as well as basic firewall capabilities. Combining the capabilities of multiple devices and appliances within a single platform helps reduce network infrastructure complexity.
What’s the difference between next gen firewalls and unified threat management?
Unified threat management (UTM) comprises security services like malware (antivirus, phishing, trojans, spyware, etc.) detection and mitigation and web content filtering (restricting user access to specific kinds of content or websites). Next generation firewalls combine UTM services with firewall capabilities to deliver comprehensive protection via a single platform.
How a next generation firewall works
Next generation firewalls offer enhanced firewall data inspection and policy enforcement capabilities, as well as additional security services such as IDS/IPS, antivirus, and content filtering.

What is the best next generation firewall?
Next generation firewalls protect the organization from breaches and cyber threats, so it’s important to validate that the next generation firewall can accomplish its advertised functions. The best next generation firewalls are rigorously tested and certified by trusted, independent technology product assurance testers, such as ICSA Labs. Verify that the testing laboratory applies objective testing criteria for evaluating product performance.
When evaluating solutions, consider that the best next generation firewall may be part of a broader solution. For example, the HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN platform combines advanced SD-WAN capabilities with identity- and role-based traffic segmentation, enforced with a built-in next gen firewall (including IDS/IPS and other security functions). HPE Aruba Networking was also the first SD-WAN vendor to attain ICSA Labs Secure SD-WAN certification, validating its built-in next generation firewall and advanced security features.
Next generation firewalls vs. traditional firewalls
Capability | Traditional firewall | Next generation firewall | Advantages of next generation firewall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Stateless | Stateful | Blocks traffic that deviates from expected norm compared to established connections |
| Visibility | Rudimentary, only lower TCP/IP layers | Deep, includes all TCP/IP layers | Enables more granular and robust analysis of traffic |
| Services | Basic | Comprehensive | Includes UTM services such as antivirus, content filtering, IDS/IPS, and logging in addition to packet filtering |
| Protection | Limited | Enhanced | Identifies, prevents, and reports a broader variety of attacks |