Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) What is Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) represents a set of innovative technologies designed for secure access to private applications. Also referred to as software-defined perimeter (SDP), ZTNA technologies use granular access policies to connect authorized users to specific applications without the need for access to the entire corporate network, establishing least-privilege app-level segmentation as a replacement for network segmentation and, unlike a VPN concentrator, avoiding exposure of the applications’ location to the public internet.
Table of Contents
ZTNA explained
The reason ZTNA adoption is becoming more prevalent is due to the need to work from anywhere, whereby every user, application and device now safely connects via the internet. This makes sense, as more business apps become SaaS-based and private apps continue to run in hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
The challenge is that the Internet is purely designed to connect things, not to block them. With a proper IP address and outbound call capabilities, all devices can communicate through the Internet. Threat actors exploit organizations that do not have the proper Zero Trust strategies in place.
Unlike VPNs or firewalls, ZTNA services are designed to securely connect specific entities to each other, without the need for overall network access. In most cases these are employees and third-party users connecting from home, on the road, or in the office. But this is not limited to just users; ZTNA can also apply to application-to-application traffic as well in the form of microsegmentation.
Key concepts of ZTNA
- Zero Trust Foundation: ZTNA is built upon the principle of Zero Trust, which means that no user or system is trusted by default, regardless of where or how they are connecting. Every access request must be fully authenticated, authorized, and encrypted before granting access.
- Application-Centric Access: Unlike traditional network access that grants access to the network, ZTNA ensures that access is given only to specific applications. This is achieved through outbound-only connections, which reduces the attack surface by not exposing the corporate network to the internet.
- Least-Privilege Access: ZTNA enforces the principle of least privilege by providing users with the minimum level of access necessary to effectively do their job. This is done through granular access policies that are consistently and globally applied across the organization, regardless of the user’s location.
- Cloud-Native for Speed and Scalability: To ensure access is both fast and reliable, ZTNA leverages cloud infrastructure. This allows for scalability to meet varying bandwidth demands and ensures that users can instantly connect to the applications they need without compromising security.
What are the key features of ZTNA?
- Identity-Based Access: ZTNA consumes and verifies the identity of users and devices before granting access. It uses authentication and authorization from your existing IDP provider to ensure only legitimate users can access resources.
- Granular Access Control: Instead of granting blanket access to a network, ZTNA enforces fine-grained access to specific applications or services based on user roles, device posture, and contextual factors.
- Least Privilege Principle: Access is limited to only what is necessary for the user to perform their tasks, minimizing the attack surface.
- Application Segmentation: ZTNA ensures that users and devices can only access the specific resources they are authorized for, preventing lateral movement within a network with zero trust policies rather than complex network segmentation.
- Continuous Verification: ZTNA continuously monitors and verifies user activity and device health. Access may be revoked if a user's session becomes suspicious or a device's security posture changes.
- Remote and Hybrid Work Support: ZTNA is ideal for organizations with remote or hybrid workforces, providing secure access to applications regardless of the user's physical location.
- Cloud-Native: ZTNA is often cloud-based and integrates with modern enterprise environments, including SaaS applications, public clouds, private clouds, and private data centers.
How ZTNA works
ZTNA creates a secure, encrypted connection between the user's device and the private application or service they need to access. It typically involves:
- Authentication: The user provides credentials, and their identity is verified through multi-factor authentication (MFA) or identity providers (IdPs).
- Device Validation: The device is assessed for compliance with security policies (e.g., OS version, antivirus status, etc.).
- Policy Enforcement: Once authenticated, access is granted based on predefined zero trust policies that consider the user's role, device security, location, and other contextual factors.
- Application-Specific Access: ZTNA ensures users only see and access the applications they are authorized for—no visibility or access into the rest of the network.
What are the benefits of ZTNA?
- Enhanced Security: ZTNA operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," which significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. By enforcing strict identity verification and contextual access controls, ZTNA ensures that users and devices are continuously authenticated and authorized before accessing any resource. This minimizes the chances of lateral movement within the network, even if an attacker gains initial access.
- Reduced Attack Surface: One of the core strengths of ZTNA is its ability to make applications and services invisible to unauthorized users. By hiding internal resources behind authentication layers and only exposing them to verified identities, ZTNA significantly limits the potential entry points for attackers. This "dark cloud" approach ensures that even if a system is targeted, it remains inaccessible without proper credentials and context.
- Improved User Experience: Unlike traditional VPNs that often require manual connections and can slow down performance, ZTNA offers a more seamless and transparent experience. Users can securely access applications from any location or device without the need for cumbersome VPN clients. This leads to faster access times, fewer disruptions, and a more intuitive workflow—especially beneficial for remote and hybrid work environments.
- Scalability: ZTNA is designed to support dynamic and distributed IT environments. Whether your organization is expanding its cloud footprint, supporting a growing remote workforce, or integrating third-party vendors, ZTNA can scale effortlessly. Its cloud-native architecture allows for easy deployment and management across multiple environments, reducing the complexity of traditional network security models.
ZTNA use cases
- VPN Alternative for Work from Anywhere: Use ZTNA to replace remote access VPNs that are typically used to connect remote users to a network, and deliver a faster, more secure experience while doing so.
- In-office Employee Access: Avoid inherently trusting on-premises users, and leverage publicly hosted Zero Trust brokers, or private brokers deployed within your own environment, for least-privilege access with simpler segmentation, faster user experience, easier compliance.
- Securing Third-party Access: Use agentless access to securely enable business ecosystem partners, suppliers, vendors, and customers to access critical business data, without granting access to the entire corporate network.
- Accelerate IT Integration During M&A or Divestitures: ZTNA helps accelerate the process of each down from 9-14 months, to just days or weeks by avoiding the need to consolidate (or split) networks, to deal with network address translation (NAT) for overlapping IPs, or to stand up a VDI infrastructure.
- VDI Alternative: Avoid the high costs, scalability issues, and latency of traditional VDI by replacing complex virtual environments with ZTNA. ZTNA delivers secure, seamless remote access through direct, policy-based connections to applications—based on user identity, device posture, and context.
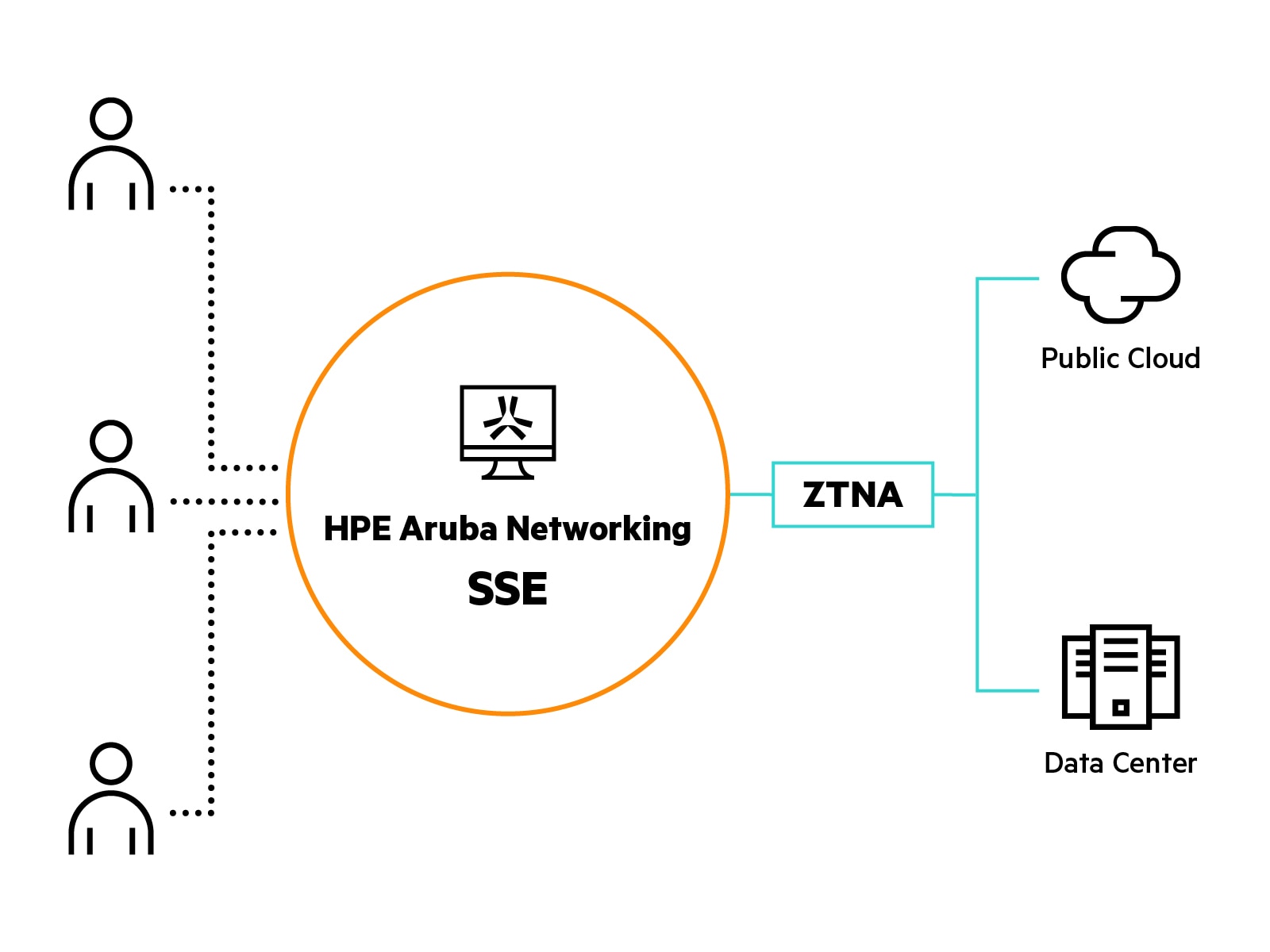
HPE Aruba Networking ZTNA
As part of the HPE Aruba Networking SSE platform, HPE Aruba Networking ZTNA provides a modern alternative to traditional remote access VPN solutions by providing secure global connectivity for any user, any device, and any private application—with zero trust.
As mentioned, ZTNA is an integral component of the HPE Aruba Networking Security Service Edge (SSE) platform. However, the overarching platform brings the power of ZTNA, SWG, CASB and Digital Experience monitoring into a single cloud-delivered solution, with one easy-to-use pane of glass to manage it all.