Multi-cloud Networking (MCN) What is Multi-cloud Networking (MCN)?
Multi-cloud networking enables the design, deployment, and operation of a network in multiple public cloud environments. MCN products enable consistent network policy, security, governance, and visibility across multiple cloud environments via a single point of management.
Multi-cloud differs from hybrid cloud, which blends the use of private and public cloud environments, typically from one provider. Multi-cloud can include private and/or public clouds but uses the best services from various providers to create a custom solution for an organization’s specific needs.
Table of Contents
Multi-cloud networking explained
Multi-cloud networking (MCN) provides automated, policy-based networking for connectivity and network services of distributed workloads in and across multiple clouds. MCN solutions, provided as network software or as a service, are managed, on demand, elastically scalable, highly available, and secure.
MCN enables enterprises to control, secure, and manage their data on networks traversing multiple private and public cloud resources and data centers. MCN architectures are software based and can intelligently connect disparate IT resources while providing control, visibility, and security over network connections.
Multi-cloud often incorporates at least two cloud services within a single architecture—in other words, different cloud stacks for different tasks, such as Google Cloud Platform for internal apps and Amazon Web Services (AWS) for customer-facing apps.
How does multi-cloud networking work?
MCN technology provides the capability to build logical, software-defined, secure network to cloud applications across multiple private clouds, data centers, SaaS providers, and public clouds. MCN solutions extend into and across leading public cloud providers including AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Alibaba Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
MCN offerings include low-code optimizations to simplify networking across disparate clouds, mitigating the complexity, operational burden, and associated costs of disconnected cloud APIs and cloud-specific network constructs. MCN solutions also help optimize network performance in and across clouds.
Using a single cloud provider can cause vendor lock-in by deliberately making it complex and expensive to migrate applications. MCN helps avoid vendor lock-in and complexity and creates infrastructure autonomy in three ways:
- MCN allows the use of multiple vendors for different workloads, making it simple and low cost to switch to another provider if one vendor raises prices or experiences an outage.
- MCN provides more control over data by storing it in different locations and limiting which vendors have access to it. This keeps sensitive data off public clouds where it could be vulnerable to hackers.
- MCN facilitates customization of infrastructure to meet business needs. Using multiple vendors allows selection of best fitting solutions rather than having to force a single vendor’s solutions to meet requirements.
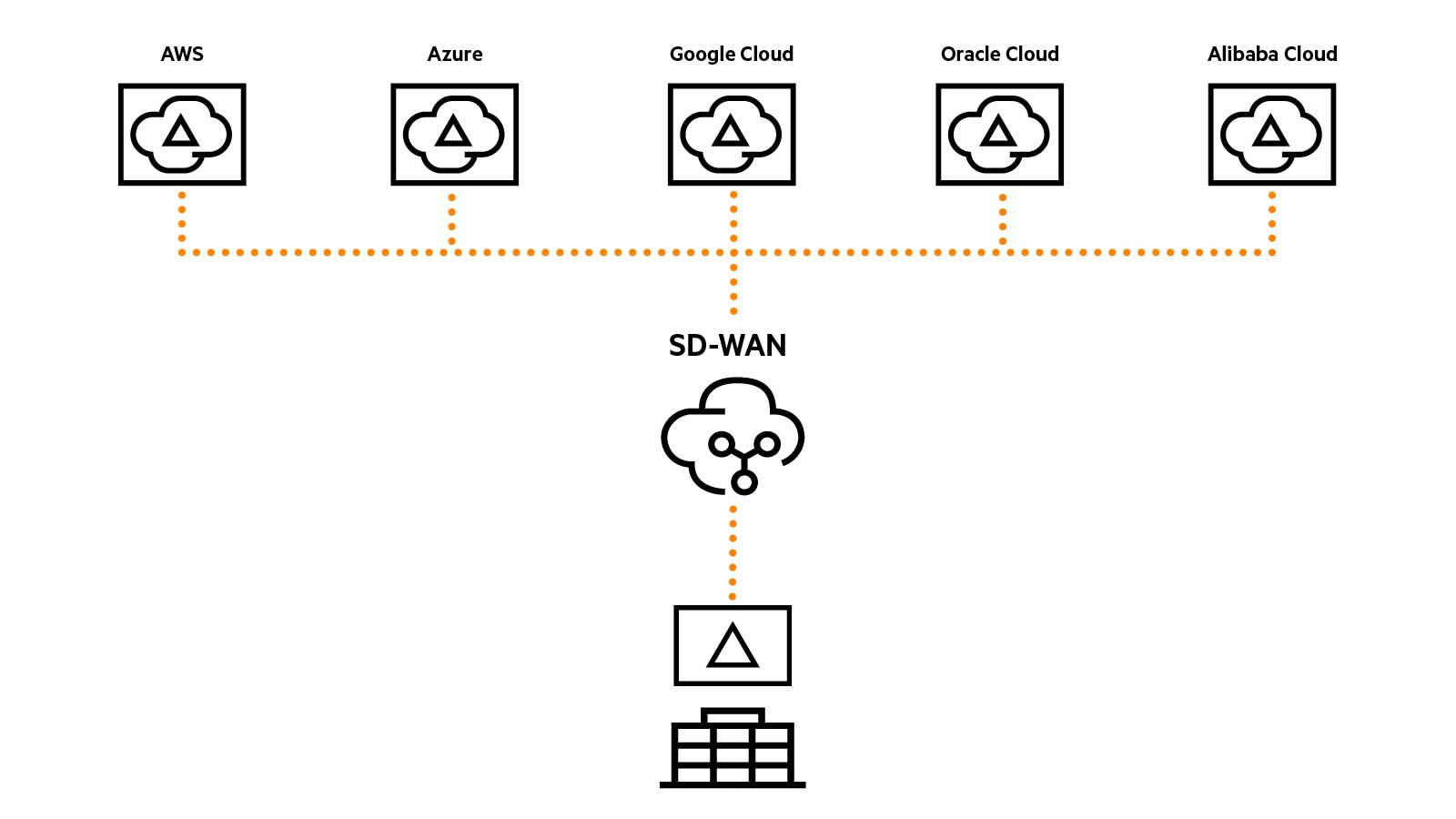

What are the benefits of multi-cloud networking?
- Mitigates business risk from a disaster by distributing data and applications across multiple clouds instead of with one single public cloud provider.
- Enables organizations to optimize ROI by taking advantage of the unique capabilities of each cloud platform to leverage the strengths of each platform, such as increased scalability or lower costs.
- Provides greater flexibility and agility, allowing businesses to adapt quickly and easily to changing needs by customizing their infrastructure based on application requirements.
Multi-cloud networking use cases
Here are three common MCN use cases that drive networking requirements:
- Siloed applications: One of the most common multi-cloud networking implementations today addresses cases of applications hosted with different IaaS providers, causing siloes. MCN allows choosing the most cost-effective option for each application from multiple vendors. This arrangement, however, can make IT management more complex, since maintaining multiple console logins and configurations requires cloud infrastructure IT expertise.
- Disaster Recovery (DR): DR is an important use case for because it enables IT to shift applications that run on a primary cloud to a secondary cloud if the first one cloud goes down. This redundancy provides increased uptime but can be more expensive to maintain.
- Workload Mobility: MCN enables enterprises to have DR automated to shift workloads to a second cloud provider and to only be activated when an outage occurs. Workload mobility refers to the ability to move workloads (the computing tasks that make up an application) between different cloud environments. MCN enables IT staff to easily migrate or move workloads from one cloud provider to another cloud provider from an orchestration console that has pre-set cloud networking policies.
Building a multi-cloud networking solution with SD-WAN
Initially, SD-WAN was limited to applications egressing from branch locations. Conceived as a way to more efficiently and cost effectively connect branch offices to cloud services or corporate networks, SD-WAN became a better, smarter router for the edge. In the past several years, enterprise SD-WAN requirements have evolved to include direct branch-cloud connectivity.
SD-WAN enables MCN by providing direct connectivity to the cloud, thus extending capabilities like application intelligence, visibility, and control to the last mile in the cloud. In the past several years, this has expanded as SD-WAN extended further into the cloud with deployment of virtual SD-WAN appliances within public cloud providers infrastructure.
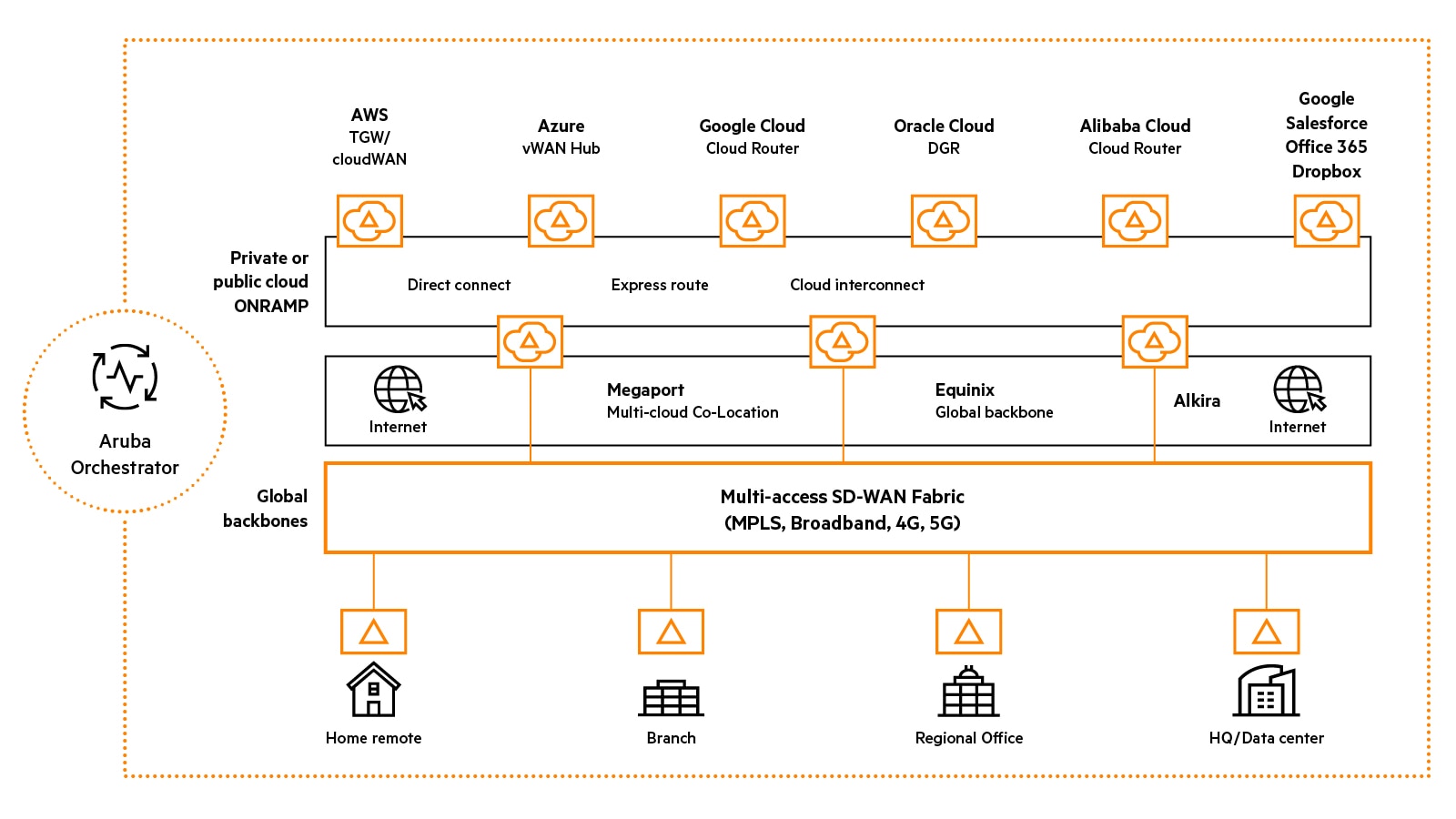
How does HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN platform support multi-cloud networking?
HPE Aruba Networking added multi-cloud networking functionality to expand on the original mission of HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect, its SD-WAN platform. An example of this would be the deployment of an EdgeConnect virtual appliance into a cloud environment, allowing customers to build an overlay network into any cloud service, including the “Big Five” (Alibaba Cloud, Amazon, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Oracle). EdgeConnect SD-WAN multi-cloud platform supports a global SD-WAN fabric that enables users to interconnect from any EdgeConnect SD-WAN enabled edge location to applications across multiple clouds, ensuring end-to-end application performance across the fabric. Customers can use an HPE Aruba Networking overlay SD-WAN fabric to tie several cloud networks together, instantly building a scalable global multi-cloud network.
SD-WAN multi-cloud networking also leverages application programming interfaces (APIs) to build automated orchestration and visibility of cloud application workloads from a SD-WAN platform. EdgeConnect SD-WAN has been integrated with leading public cloud provider backbone networks such as AWS CloudWAN, Microsoft Virtual WAN (vWAN) and Google Network Connectivity Center and also middle-mile cloud exchanges such as Equinix, Megaport, and Alkira.