Wi-Fi What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi (often incorrectly written as wifi or WiFi) is actually not an acronym. The Wi-Fi Alliance coined the term based on the IEEE 802.11 standard. It defines the protocols that enable communications over wireless routers and access points and is continuously updated to respond to increased demands on the network.
Time to read: 3 minutes 7 seconds | Updated: October 31, 2025
Table of Contents
Wi-Fi connectivity explained
Wi-Fi connectivity allows Wi-Fi devices like laptops, cellular phones, sensors, and equipment like printers and video cameras to interface with the internet via a wireless router or access point, between APs (mesh), or between client devices (ad hoc). Wireless routers are typically found in homes, provided by your cable/internet provider, and combine the capabilities of a router with a wireless access point.
What is 802.11?
802.11 is the standard defined by IEEE and includes amendments to support technology advancements.
What is Wi-Fi Certification?
Completing the certification from the Wi-Fi Alliance, an independent industry organization, signifies that the product has been thoroughly tested and meets the all the requirements associated with a specific Wi-Fi standard. Wi-Fi certification ensures that devices and access points (APs) from different vendors interoperate reliably, securely, and according to the standard such as Wi-Fi 6.
What are the key Wi-Fi use cases?
1. Mobility: Wi-Fi allows for greater mobility across client devices such as laptops and cellular devices. In the past, many campus users relied on wired connections which tether users to their desk and limit the mobility needed for effective collaboration.
2. IoT onramp: Wi-Fi can be used as an IoT transport platform, eliminating the need for overlay gateways. APs are typically located on the ceiling, providing an ideal vantage point for IoT communication whether it is via Bluetooth (BLE) or 802.15.4 (Zigbee).
3. Cellular offload: With the introduction of 5G, the use of Wi-Fi as a cost-effective way to offload cellular communications is increasing. Solutions like Air Pass that use Passpoint technology provide a seamless handoff from cellular to Wi-Fi networks without requiring additional logins or click throughs. This use case is increasingly important as 63% of enterprise cellular traffic is offloaded to Wi-Fi (Wi-Fi Alliance).
How can I secure my Wi-Fi network?
To strengthen your security posture, leverage both Wi-Fi 6/6E capabilities and role-based access controls. WPA3 and Enhanced Open are capabilities of Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) that enhance user and guest encryption. Policy Enforcement Firewalls use role-based access control and deep packet inspection to isolate and segment traffic as part of a Zero Trust Network and SASE framework.
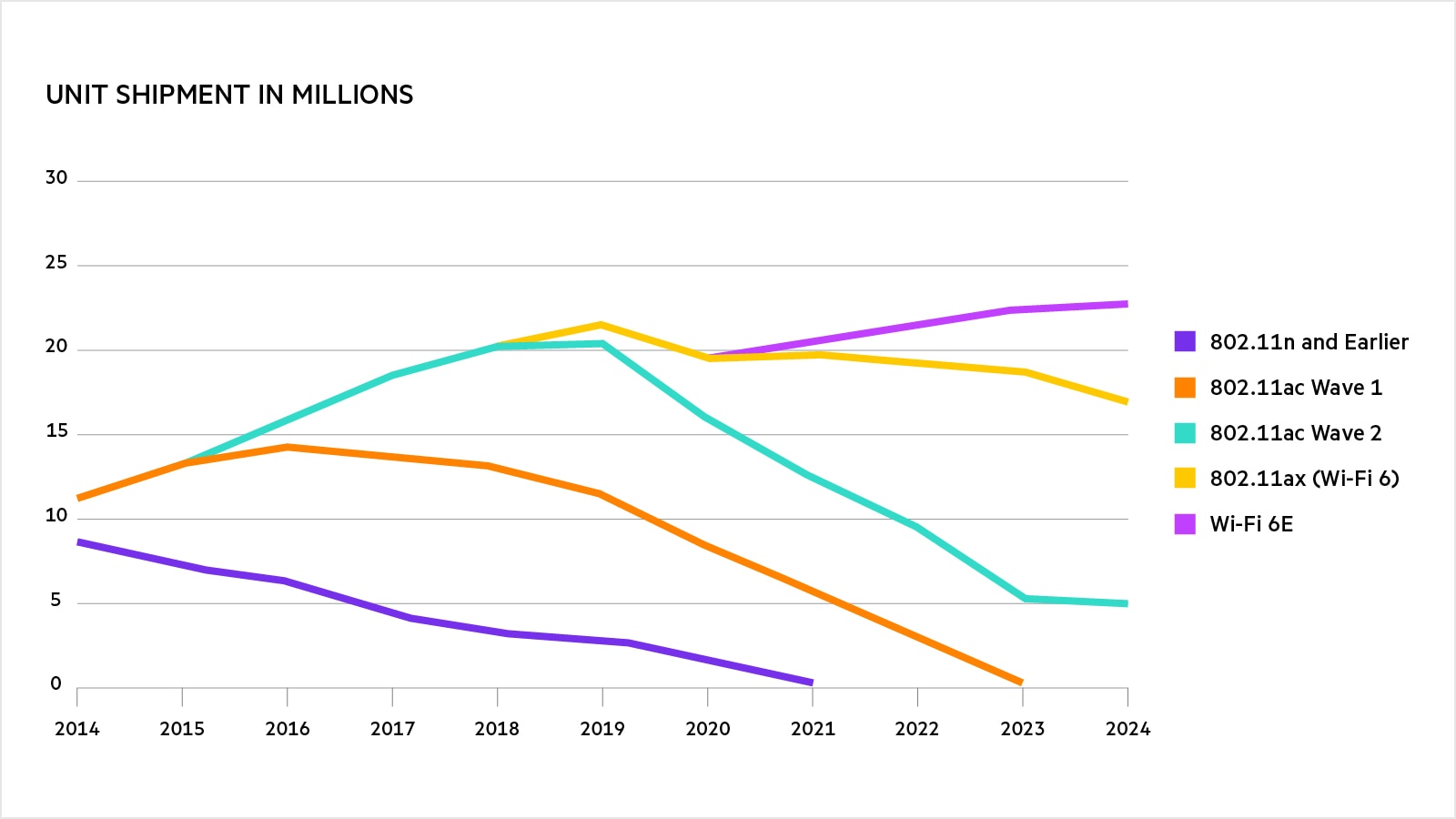
Wi-Fi new technology adoption
Enterprise adoption of new standards varies. Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E adoption has been faster than previous technology introductions due to the perceived value of the enhancements in Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E to support increasing numbers of client and IoT devices and to meet user expectations for performance.
Wi-Fi standards
IEEE classification
802.11 amendment | IEEE clasifications for 802.11 | Wi-Fi alliance name |
|---|---|---|
| a, g | Non-HT (Non-High Throughput) | None |
| n | HT (High Throughput) | Wi-Fi 4 |
| ac | VHT (Very High Throughput) | Wi-Fi 5 |
| ax | HE (High Efficiency) | Wi-Fi 6 |
| ax in 6 GHz | HE (High Efficiency) | Wi-Fi 6E |
| be (Future) | VHE (Very High Efficiency) | Wi-Fi 7 |
How do I choose a Wi-Fi vendor?
Consider networking and Wi-Fi vendors that:
- Demonstrate industry leadership as recognized by leading analysts such as Gartner, Forrester, and IDC.
- Deliver built-in security with unified policy enforcement across wired and wireless networks.
- Simplify operations by using AI and machine learning to automate optimization and provide actionable recommendations to remediate issues.
- Offer secure, energy efficient IoT capabilities to enable you to leverage APs as an IoT connectivity platform using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Zigbee, or USB ports.
- Provide the flexibility to manage on-prem or in the cloud and to deploy with or without gateways.
- HPE offers Wi-Fi access points solutions by both HPE Aruba Networking and HPE Juniper Networking.