Private 5G What is private 5G network?
Private 5G allows enterprises to deploy dedicated cellular resources based on the latest 3GPP standards for mobile networks. It complements Wi‑Fi to provide a customized experience under enterprise control, over large areas, and with dedicated resources—supporting deterministic mobility, and latency-sensitive applications.
Table of Contents
Private 5G vs 5G explained
5G is the fifth generation of cellular technology and is based on 3GPP standards. It builds on the innovation of 4G (also known as LTE) to significantly increase speed, reduce latency, and improve the flexibility of wireless services to better serve consumers and digitalize businesses. End user devices must be 5G compatible to run on 5G networks since the standard is not backwards compatible.
Private 5G leverages the same technology standard as public 5G. However, the "private" in private 5G signifies that the cellular network is deployed to meet the needs of a specific enterprise, under control and with dedicated access to private resources. It offers greater reliability and security since the resources are dedicated to a specific entity. Unlike Wi-Fi which uses unlicensed spectrum, private 5G relies on a network slice from a public network or lightly licensed spectrum such as CBRS
What is private LTE?
Private LTE enables enterprises to deploy a cellular network with dedicated access to private resources based on the 3GPP standard for LTE/4G. Private 5G represents the evolution of cellular technology that offers faster speeds and lower latency than private LTE.
What is the difference between 5G and private 5G?
Public 5G is a shared resource provided by mobile network operators to their subscribers, whereas private 5G provides dedicated enterprise access to private resources under enterprise control.
How does private 5G work?
Private 5G consists of 3 key components and can be managed on-prem, in the cloud, delivered as a service or through a hybrid model:
- 5G mobile core
The management layer of the private 5G network, exposed to the enterprise through the same tools used to manage existing Wi-Fi networks.
- Radio access network (RAN)
The local radio network made up of small cells, typically leveraging shared spectrum identified specifically for enterprise use.
- 5G client devices
The mobile endpoints of the network with physical or eSIM credentials.
The private 5G network can be deployed in the public or private cloud, on-prem, or in a hybrid model.
What models exist for private 5G?
There are several models including:
- Enterprise-owned private 5G: The organization owns and manages all the equipment and leverages shared spectrum identified for private enterprise use.
- 5G as a service: A service provider or system integrator deploys the network and can manage it on behalf of an enterprise.
- Neutral host: In either of the above deployment models, the private network accepts inbound roaming of subscribers from a public cellular network, bridging local gaps in cellular coverage.
Private 5G vs private LTE
Both 5G and LTE are 3GPP standards for cellular. LTE, also known as 4G, refers to the generation immediately prior to 5G. As such, 5G offers architectural and performance enhancements designed to address specific enterprise networking requirements. It does this based on three fundamental technologies to improve spectral efficiency:
- Flexible core network architecture.
- 5G radio.
- Mobile edge computing, which moves resources from the core to closer to where data. is consumed and generated.
What is the market for private 5G?
The market is estimated to reach $9B by 2028, according to Analysy Mason (Analysys Mason, Telecoms capex: worldwide trends and forecasts 2018–2028, 2024).
What are the key use cases for private 5G?
Private cellular networks (LTE and 5G) represent an emerging market with most investments thus far in energy, mining, manufacturing, transportation, logistics, government, and public venues. As private cellular networks become more closely integrated with existing Wi-Fi networks, opportunities open across a broader range of markets, including coverage over larger areas, segregating guest from back-of-house traffic, ensuring more deterministic mobility for high-velocity IoT clients, or filling gaps in public network coverage. Examples include:
- Retailers can operate mobile point-of-sale terminals and inventory scanners, connect building IoT systems, feed ruggedized tablets on forklifts, and power robotic warehouse systems
- Manufacturers can use wirelessly enabled power tools to record every aspect of a product’s creation as it moves down the line, and apply machine vision systems for automated quality inspection
- Public venues can perform ticket scanning, enable push-to-talk (PTT) voice communication between staff members, and sports teams can provide secure sideline data terminals for real time decision making
- Hospitals can deliver latency-sensitive medical telemetry to nursing stations and electronic medical record servers, and provide PTT voice communication for clinical staff, and enhance in-building cellular service for patients, families, and staff
- Mining and heavy industry can use private 5G to cover large areas without the need to run cable.
What is the HPE Aruba Networking approach to private 5G and Wi‑Fi?
HPE Aruba Networking believes that enterprises will rely on both private cellular networks and Wi-Fi in the future to meet their wireless needs. Enterprises have told us that they do not want to deploy private cellular networks and Wi-Fi in silos and prefer a combined solution allowing organizations to manage them with existing tools and on familiar terms.
The acquisition of private 5G leader Athonet gives HPE a boost in the 5G cloud-native core software with the ability to deliver HPE Aruba Networking Private 5G on-premises, wholly in the cloud, or in a hybrid manner. To make it easier for enterprises to adopt private 5G, HPE has also announced an all-in-one solution that includes a cloud-native dashboard, core, hardware appliance, small cells, and SIM or eSIM cards. The objective is to make private cellular as easy to deploy as Wi-Fi.
What is 5G AI?
5G plays an important role in AI. AI is driving more challenges around growth of traffic, performance, and latency. AI generates more data, and that data cannot sit in a single location. It is truly dynamic, and it must be acted upon multiple times, often in multiple locations, which in turn drives a significant increase in data loads in customer network environments.
To be able to collect all data—no matter where it’s generated—enterprises need to implement the broadest set of connectivity options including private 5G. Because of the parallel processing inherent in AI, latency must be kept to a minimum. Private 5G delivers wide area coverage across a broad range of end user devices, yet is highly reliable with very low latency.
How do client devices mover between 5G and Wi‑Fi networks?
HPE Aruba Networking Air Pass enables Wi-Fi enabled devices with SIM credentials to automatically connect to local Wi-Fi networks. The combination of the Air Pass service, Passpoint authentication, and Wi-Fi Calling (WFC) ensures robust in-building and campus cellular coverage, delivered over Wi-Fi, while also aligning SIM-based identities with corporate credentials.
What is 5G standalone (also known as 5G SA)?
As background, when 5G first was rolled out, it typically relied on 5G non-standalone core, also known as 5G NSA. By using a 4G (LTE) core and 5G RAN, this intermediate step allowed service providers to roll out 5G without replacing the core backend systems while still delivering faster speeds and better reliability than a full 4G network. In contrast to 5G NSA, 5G standalone uses a 5G core and 5G radio with cloud-native architecture for greater flexibility and dynamic resource allocation. Today’s focus is on rolling out 5G standalone implementations.
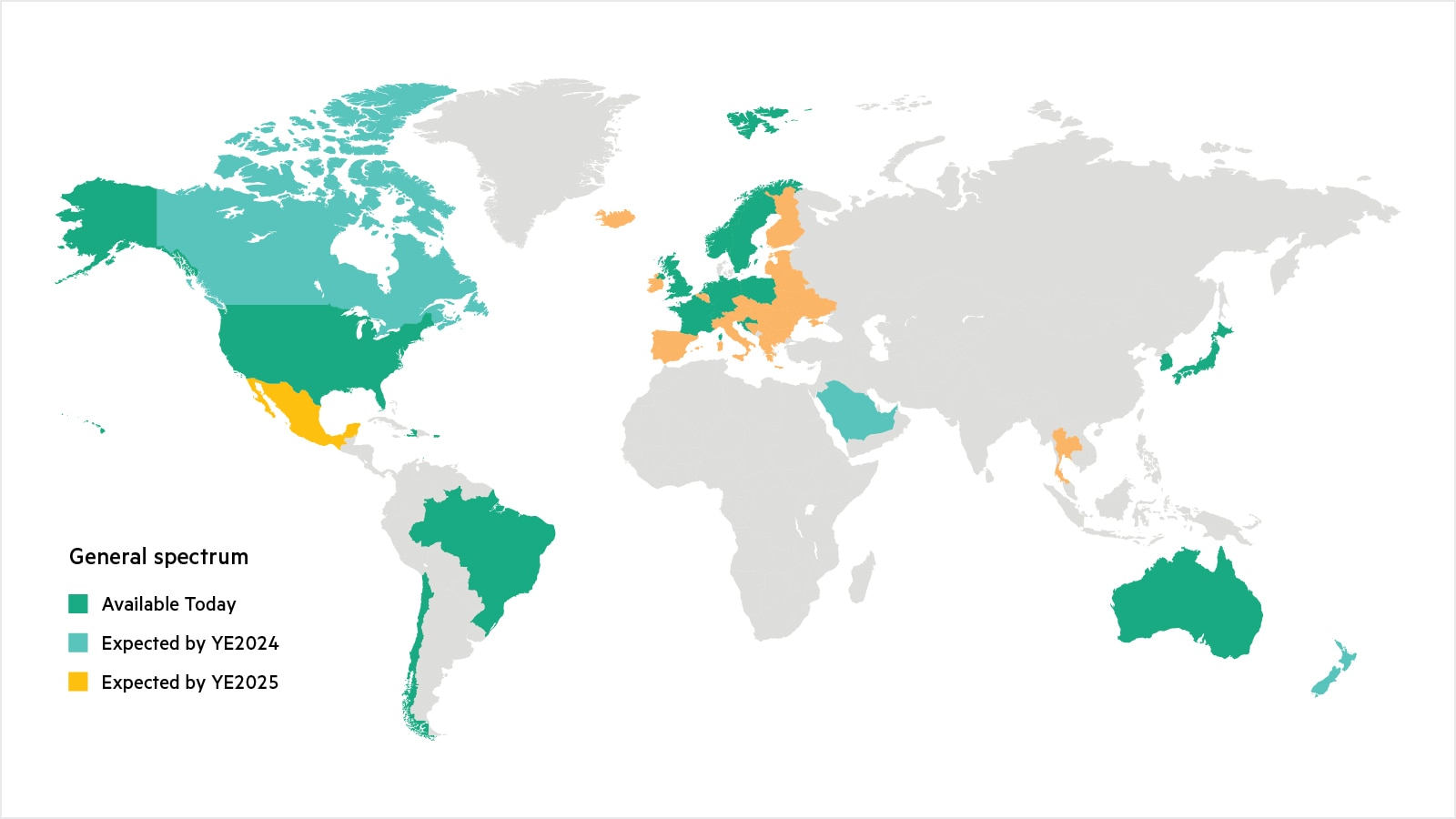
What cellular spectrum is used in private 5G?
Either shared or lightly licensed spectrum can be used in private 5G implementations. In countries such as the US, unlicensed spectrum known as CBRS or band 48 can be used for private 5G. In other countries, where there is no unlicensed spectrum available, cellular spectrum is made available by the mobile network operators using network slicing. The map below shows the availability of unlicensed or lightly licensed spectrum.
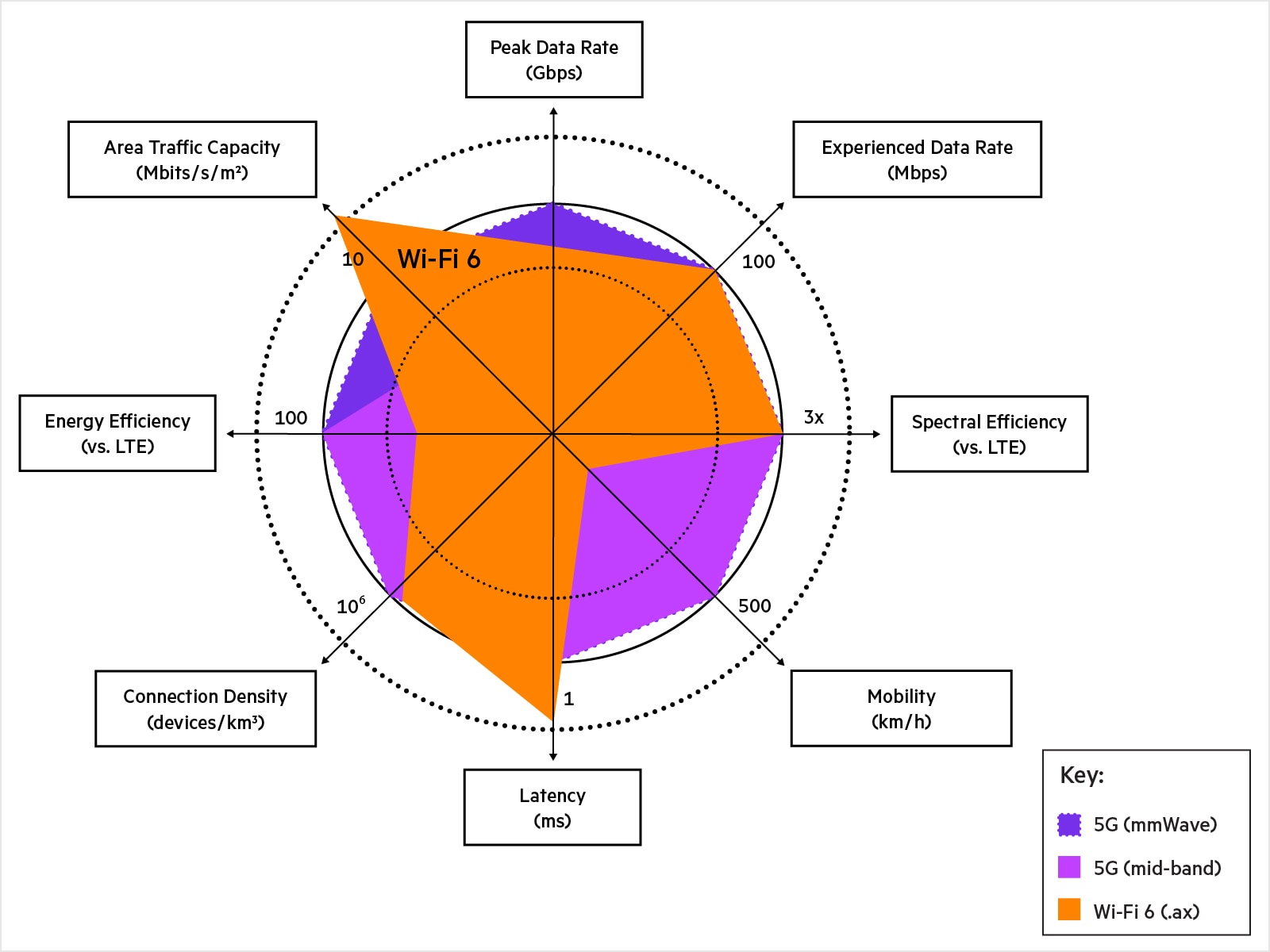
Benefits of private 5G vs Wi‑Fi
Private 5G and Wi‑Fi have often been discussed in terms of either/or. However, the two are highly complementary and enterprises are exploring new ways to use the private 5G and Wi‑Fi 6/Wi‑Fi 6E in tandem.
Private 5G and Wi‑Fi are complementary:
- Private 5G provides wider area coverage, high-velocity mobility, and deterministic network access.
- Wi‑Fi 6 and Wi‑Fi 6E (802.11ax) deliver the highest network capacity in dense deployments, particularly indoors.
Some industry examples:
- Large public venues are using dedicated private 5G for secure, back-end applications while reserving high-capacity Wi‑Fi for fan activities.
- Warehouses are using private 5G to provide seamless roaming over large areas for fast-moving robotic/autonomous vehicles and Wi‑Fi 6/6E for office use and IoT applications such as touchless door locks.
- Higher education institutions are using private 5G for campus security cameras and Wi‑Fi for high-density lecture halls and dormitories.
- Governmental organizations are using private 5G for highly classified applications and Wi‑Fi for indoor mobility and guest access.